Importance of Uninterruptible Power Supply

One of the main objectives of an electrical power system is the continuous power supply to the load. However, achieving reliability is not easy that is there is a high chance of non-availability of supply (due to fault) to load. Severe voltage fluctuations are also a topic of concern in power systems as these variations result in equipment damage. So, the power system defines its distribution load in two ways: critical and non-critical.
For non-critical loads (residential loads mostly), there is a relaxation of unavailability of supply for a certain time frame. But for critical loads (lifesaving equipment in hospitals, data centers, or SCADA systems in power plants or industries) the supply should be available at all times and almost zero tolerance against voltage variation is considered. In this regard, facilities add up an additional backup power supply (Small Generator and renewable energy source) supported with a battery backup which is provided using a UPS (Uninterruptable Power Supply).
This blog contains all the useful information related to UPS, its types, its application, and how it is integrated with a running power system.
What is an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) and why it is needed?
An uninterruptable power supply (also called uninterruptable power source, battery/flywheel backup, or UPS) is an electrical equipment that acts as a source immediately as the main power gets failed due to any interruption. UPS usually stores energy in batteries and flywheels.
In spite of providing a power source, it can also protect the load from system variation (that can damage sensitive equipment) which includes transient voltages, frequency instability, and harmonic distortion as it provides pure sinusoidal wave voltages to load.
👉🏼 Learn more about the Importance of Power Quality in the Power System to enhance the efficiency of the system and reduce Power Losses along with Operating Costs.
Common Causes of Power Outages
There are many reasons for power outages. Some are listed below:
- Natural: a tree collided with a power line due to bad weather or a storm.
- Vehicle: a truck or car collided with poles carrying power lines.
- Animals: one of the probabilities of power failures is lizards and snakes somehow enter the power panels and cut off the cables or become a short path for fault. Birds also cause short circuits in transmission lines.
- Outdated Equipment: every piece of equipment has a certain lifetime also equipment requires proper maintenance. If this equipment is not properly monitored and maintained then there is a high chance of power outages due to equipment failure.
We recently published a blog on The Importance of Equipment Maintenance Plan for Electrical Power Systems. Checked it out to grasp the information available in this blog.
Components of UPS
The following main components are mostly available in UPS:
- Rectifier: to convert AC into DC
- Inverter: to convert DC into AC
- Battery: supplies power when supplies are cut off
- Transfer Switch: for transferring load from main supply to backup supply (battery, capacitor bank, flywheel).
The above-mentioned components are representing a simple UPS construction. Somehow, there are further components added according to different requirements and applications.
How does an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) work?
Normally UPS takes the main AC input and converts it into DC. The DC output is used to charge the battery bank. Some UPS consist of charge controllers in order to control over charging of the battery. The battery power can be used by the load by switching to the inverter using a transfer switch. Here the Inverter is used to convert the battery power to AC as the loads are mostly AC.
Difference between UPS and Inverter?
Most people get confused and consider UPS and inverter as the same equipment. UPS is a complex system with having inverter as one of the components. We can use UPS as an inverter by just disconnecting the main AC input and taking input from the battery but we cannot use an inverter as UPS.
Technologies:
-
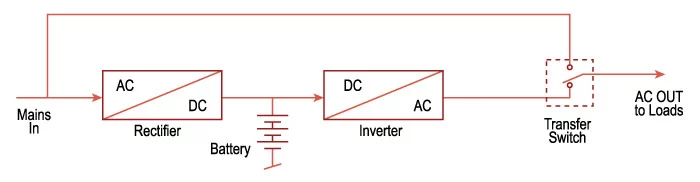
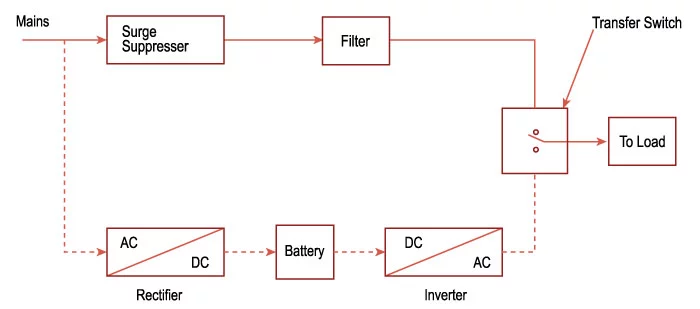
Offline / Standby (Either Offline or Standby can be used) UPS
It is the simplest UPS, in which power from the battery bank is only used as a backup, that is in normal condition the main supply not only provided power to load but also used for battery charging but firstly it is converted into DC through a rectifier.
In fault condition, the load is transferred to the battery using a transfer switch, as the load is AC, the power supplied by the battery is converted into AC using an inverter.
The transfer time from main to backup is normally 25 milliseconds. One of the key feature of such UPS is that it provides protection against surges along with battery backup.
-
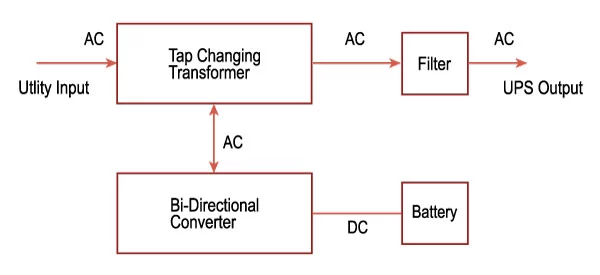
Line Interactive
These types of UPS are used for reducing voltage fluctuation by using tap changers and have filters to reduce transient loss. It can work for up to 30 minutes by maintaining the voltages using tap changing transformer.
-
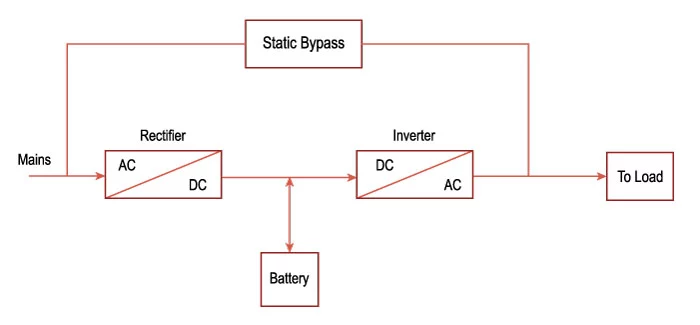
Online / Double Conversion (Online or Double Conversion can be used)
It is known as double conversion due to its characteristic of converting the main AC input into DC using a rectifier and providing that power for the battery to charge and to the inverter to convert back into AC for the connected load. At the time of power failure, the rectifier gets disconnected and the power is provided from the battery completely.
This type of system is expensive and needs good maintenance as the converter system is used all the time. They have almost negligible transfer time but due to heavy load switching and inrush current the transfer time can be 4 to 5 milliseconds.
Applications of Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS):
UPS is mostly used for systems having critical loads. Some examples include:
- Industries: some of the operations in industries required continuous power. A certain loss in a power outage can cause a great production loss.
- Power Plants: consist of SCADA and DCS, for monitoring and operation purpose. These systems require reliable power and have a UPS system integrated with them.
- Hospitals: consist of life-saving machines that require UPS for continuous power. They also play a crucial role in intensive care units
- As everything is digitalized, all the information is now being processed and saved on cloud technology. Data centers, banks, and flight simulations are pure examples of it. A power outage may result in data loss. For this purpose, UPS plays a crucial role.
AllumiaX is a licensed Engineering company headquartered in Seattle, Washington USA. We work with sub-contractors to deliver various Power System Engineering studies including DC arc flash, DC short circuit, and more. Get in touch with us or Request a Quote.

Stay Sharp & Join our Mailing List!
Subscribe to Allumiax Blog for updates on power system studies, tips, guides and insights on electrical engineering from industry leaders.